Troubleshooting Analog Voice Interfaces to the IP Network
If you are troubleshooting an analog
connection, you must understand what type of circuit and interface your
voice port is using. Analog voice port interfaces connect routers in
packet-based networks to analog two-wire or four-wire analog circuits in
telephony networks. Two-wire circuits connect to analog telephone or
fax devices, and four-wire circuits connect to PBXs. Analog voice
telephony interfaces include foreign exchange office (FXO), foreign
exchange station (FXS), and receive and transmit (E&M). Direct
Inward Dialing (DID) is a service offered by telephone companies that
enables callers to dial directly to an extension on a PBX without the
assistance of an operator or automated call attendant.
To troubleshoot analog voice interfaces, see the following sections:
If you are troubleshooting a connection to a
PBX, you might find the PBX interoperability notes useful. These notes
contain configuration information for Cisco gateways and several types
of PBXs. To access these notes, use the following website:
FXS Interfaces
An FXS interface connects the router or access
server to end-user equipment such as telephones, fax machines, and
modems. The FXS interface supplies ring, voltage, and dial tone to the
station and includes an RJ-11 connector for basic telephone equipment,
keysets, and PBXs. In Figure 10, FXS signaling is used for end-user telephony equipment, such as a telephone or fax machine.
Figure 10 FXS Signaling Interfaces

If you are having trouble with an FXS port, check the following sections:
FXS Hardware Troubleshooting
An FXS interface connects directly to a
standard telephone, fax machine, or similar device and supplies ring,
voltage, and dial tone.
Troubleshoot FXS hardware by checking the following sections:
Software Compatibility
To ensure that your FXS card is compatible with your software, check the following:
• For
network modules inserted into Cisco 2600 series, Cisco 3600 series, and
Cisco 3700 series, check the compatibility tables in the "Overview of Cisco Network Modules" chapter in the Cisco Network Modules Hardware Installation Guide.
For
network modules inserted into Cisco 2600 series, Cisco 3600 series, and
Cisco 3700 series, check the compatibility tables in the "Overview of Cisco Network Modules" chapter in the Cisco Network Modules Hardware Installation Guide.
• For
interface cards inserted into Cisco 1600 series, Cisco 1700 series,
Cisco 2600 series, Cisco 3600 series, Cisco 3700 series, and Cisco ICS
7750 platforms, check the compatibility tables in the "Overview of Cisco Interface Cards" chapter in the Cisco Interface Cards Installation Guide.
For
interface cards inserted into Cisco 1600 series, Cisco 1700 series,
Cisco 2600 series, Cisco 3600 series, Cisco 3700 series, and Cisco ICS
7750 platforms, check the compatibility tables in the "Overview of Cisco Interface Cards" chapter in the Cisco Interface Cards Installation Guide.
Cabling
Two types of cabling are supported for Cisco FXS interfaces. They are described in the following sections:

Note  For FXS connections, use a 2-wire (RJ-11) cable. A 4-wire cable can cause the second port to busy out.
For FXS connections, use a 2-wire (RJ-11) cable. A 4-wire cable can cause the second port to busy out.
RJ-11 Connectors
The two-port and four-port FXS interface cards support the RJ-11 connector. Illustrations of the connector ports are shown in Figure 11 and Figure 12. Information about LEDs can be found in the "Connecting Voice Interface Cards to a Network" chapter of the Cisco Interface Card Hardware Installation Guide.
Figure 11 Two-Port FXS Card Front Panel
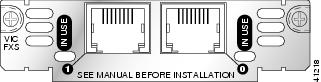
Figure 12 Four-Port FXS/DID Card Front Panel
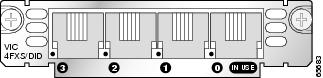
For information about the VIC-2FXS interface card, refer to Understanding Foreign Exchange Station (FXS) Voice Interface Cards, document ID 7938.
RJ-21 Connectors on the High-Density Analog Telephony Network Module
The High-Density Analog Telephony network
module supports an RJ-21 connector. This network module supports both
FXS and FXO traffic. An illustration of the connector port is shown in Figure 13. Information about LEDs and pinouts can be found in the "Connecting High-Density Analog Telephony Network Modules to a Network" chapter of the Cisco Network Modules Hardware Installation Guide.
Figure 13 High-Density Analog Telephony Network Module
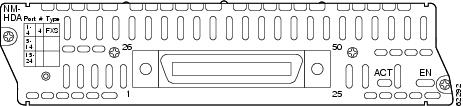
Shutdown Port
If the port is not working, be sure the port is not shut down. Enter the show voice port command with the voice port number that you are troubleshooting. The output will tell you:
• If the voice port is up. If it is not, use the no shutdown command to make it active.
If the voice port is up. If it is not, use the no shutdown command to make it active.
• What parameter values have been set for the voice port, including default values (which do not appear in the output from the show running-config command). If these values do not match those of the telephony connection you are making, reconfigure the voice port.
What parameter values have been set for the voice port, including default values (which do not appear in the output from the show running-config command). If these values do not match those of the telephony connection you are making, reconfigure the voice port.
Disabling a Port on a Multiple Port Card
If you shut down a port on a multiple-port
card, you can disable all of the ports on that card. If only one port is
bad and the others are working, in many cases you can disable the bad
port and then use the working ports until a replacement arrives. To
disable a bad port, use one of the following methods:
• On
a Cisco universal gateway, such as the Cisco AS5350, Cisco AS5400,
Cisco AS5800, and Cisco AS5850, busy out the port using the busyout
command. This setting allows the port to be taken out of service
without disrupting the Cisco IOS configuration. See the product
documentation for details:
On
a Cisco universal gateway, such as the Cisco AS5350, Cisco AS5400,
Cisco AS5800, and Cisco AS5850, busy out the port using the busyout
command. This setting allows the port to be taken out of service
without disrupting the Cisco IOS configuration. See the product
documentation for details:
• On other Cisco gateways, remove the port from the dial peer. Refer to "Dial Peer Features and Configuration" in the Dial Peer Configuration on Voice Gateway Routers document to configure the dial peer.
On other Cisco gateways, remove the port from the dial peer. Refer to "Dial Peer Features and Configuration" in the Dial Peer Configuration on Voice Gateway Routers document to configure the dial peer.
Ring Voltage Problems
Telephone exchanges and FXSs need to supply DC
battery and AC ringing to enable the connected telephone equipment to
transmit speech energy and to power the telephone equipment's ringing
device. This section discusses what voltages are supplied by various
Cisco FXS interfaces and how to overcome some known issues regarding
voltage levels.
Ringing Voltages
The industry standard for PBX and key systems
requires that the ring detection circuit be able to detect a ringing
signal as low as 40 Vrms. This voltage takes into account the effects of
load and cabling voltage drop on a ringing signal generated from a
central office (CO). Conversely, the CO (exchange) must supply ringing
with enough power to drive the maximum load over the maximum cable
length. In order to meet this requirement, a CO-based unit must present a
ringing signal with an amplitude of approximately 85 to 100 Vrms. Cisco
voice gateways are intended for use as on premise services (ONS)
equipment that is colocated or fairly close to equipment that detects
ringing, so it can therefore use a lower ringing voltage and still meet
the 40 Vrms 5 Ringer Equivalence Number (REN) requirement.
Idle Battery Voltage
Cisco voice gateways were designed for ONS
connections and by default the FXS interface supplies either -24 Vdc or
-36 Vdc idle battery, whereas off premise services, such as a CO, would
require voltages of -48 V because it might have to interconnect over
much greater cable lengths. Certain Cisco FXS interfaces can be
configured to supply higher voltages.
Idle Line Voltages
Table 24 shows idle line voltages supplied by various Cisco gateway FXS interfaces.
Ring Voltage Problems
Voltage problems can cause three types of problems:
Certain automated devices, such as fax
machines, answer machines, multiline phones and voice mail systems, look
at the line voltage in order to deduce if the line is busy or idle. If
another device is off hook, then the line voltage drops, and the
automated system does not answer or initiate a call. If the threshold
being used is close to -24 V or higher, this can cause the device not to
work as expected.
Certain phones might not ring when the default ring voltage and ring frequency are applied from the Cisco FXS interface.
Answering and Call Initiation Problems with Automated Telephony Devices
In voice port configuration mode, configure the idle-voltage command on the voice port of the FXS to increase idle battery voltage from -24 V to -48 V. The idle-voltage low setting designates -24 V and the idle-voltage high setting designates -48 V.

Note  This option is not available on VG248, VIC-2FXS, and WS-x6624 FXS interfaces.
This option is not available on VG248, VIC-2FXS, and WS-x6624 FXS interfaces.
Ringing Problems
Phone manufacturers sometimes use frequency
filters known as antitinkle circuits to prevent ringer devices from
sounding while the user is dialing. Sometimes it is necessary to adjust
the frequency of the ring to suit the connected device.
Configure the ring frequency for Cisco modular access routers by issuing the following command:
Router(config-voiceport)# ring frequency ?
25 ring frequency 25 Hertz
50 ring frequency 50 Hertz
Configure the ring frequency for the Cisco IAD2400 platform by issuing the following command:
Router(config-voiceport)# ring frequency ?
20 ring frequency 20 Hertz
30 ring frequency 30 Hertz
To prevent ringer devices from sounding, you
can also provide a voltage threshold so that the lower voltages, which
can be produced during dialing, are ignored. Increasing the voltage can
overcome this.
Configure the DC offset voltage on Cisco IAD2400 series routers by issuing the following command:
Router(config-voiceport)# ring dc-offset ?
10-volts Ring DC offset 10 volts
20-volts Ring DC offset 20 volts
24-volts Ring DC offset 24 volts

Note  This
command sequence can be used only for Cisco IAD2400 series routers. The
24-V ring DC offset setting is available for Cisco IOS 12.2(11)T and
later releases.
This
command sequence can be used only for Cisco IAD2400 series routers. The
24-V ring DC offset setting is available for Cisco IOS 12.2(11)T and
later releases.
FXS Ring Failure in the United Kingdom
A telephone approved for the United Kingdom
might fail to ring when connected to a Cisco FXS port. The failure
results from a physical interoperability issue and is independent of
Cisco hardware or software. British Telecom did not implement RJ-11 type
connectors when it adopted plug-and-socket connection methodology.
RJ-11 connectors allow parallel connectivity for the transmission path
and the ringer circuit. They were not used because older telephones
needed to have their ringer circuits connected in series due to a
requirement for high current.
Outside the United Kingdom, ringer circuitry is
self-contained in each phone. The U.K. implementation puts the
capacitor, which provides the AC ring path, and the antitinkle feature
(prevents the bell or ringer from sounding when pulse dialing is used)
externally in the first socket, connected to the local loop.
In
the United Kingdom, certain British Approval Board for
Telecommunications (BABT) telephones fail to ring when they are
connected to FXS ports on Cisco voice-enabled routers and switches.
Outgoing calls can be made and voice communication in both directions
can be established. However, incoming calls do not ring the telephone.
These telephones functioned correctly before they were connected to the
FXS ports.
Because a proprietary connection system is
implemented, you must use an adapter to connect the telephone to an FXS
port. The adapter must be a master that contains the capacitor, or the telephone fails to ring.
For a schematic and more information, refer to Understanding Why Telephones in the United Kingdom Connected to Cisco FXS Interfaces May Fail to Ring, document ID 25800.
Unbreakable Dial Tone
A common problem encountered in a VoIP network
is being unable to break dial tone. The router seizes a line on the
local PBX but when digits are dialed, the dial tone stays. The calling
party is unable to pass the dual-tone multifrequency (DTMF) tones or
digits to the terminating device, resulting in callers being unable to
dial the desired extension or interact with a device that needs DTMF
tones such as a voice mail or an interactive voice response (IVR)
application. This problem can result from a number of sources, for
example:
• DTMF tones are not passed.
DTMF tones are not passed.
• DTMF tones are not understood.
DTMF tones are not understood.
• DTMF tones are too distorted to be understood.
DTMF tones are too distorted to be understood.
• Other signaling and cabling issues occur.
Other signaling and cabling issues occur.
Make sure the dial type is set as DTMF on both
the router and the PBX. The FXS port does not pass on the digits;
therefore, this setting is not available on an FXS port. However, this
setting can be changed on FXO and E&M ports:
Router(config-voiceport)# dial-type ?
dtmf touch-tone dialer
mf mf-tone dialer
pulse pulse dialer
For more information, refer to Inability To Break Dialtone in a Voice over IP Network, document ID 22376.
No LED When Phone Off the Hook
Verify if you have an analog or digital card.
If you have an analog card like the VIC-2FXS or the VIC2-4FXS, you might
have one of the following problems:
• The port is in a shutdown state.
The port is in a shutdown state.
• The port is in a park state.
The port is in a park state.
• The port is bad.
The port is bad.
If you have a digital card like the NM-2V, you might have bad DSPs.
Use the following procedure if there is no LED when your phone is off hook:
Step 1  Check the cable to make sure that it is RJ-11 with two pins for the FXS port.
Check the cable to make sure that it is RJ-11 with two pins for the FXS port.
Step 2  Test the LED using a different phone.
Test the LED using a different phone.
Step 3  Check your Cisco IOS version to make sure that the feature set is either IP Plus or Enterprise Plus.
Check your Cisco IOS version to make sure that the feature set is either IP Plus or Enterprise Plus.
Step 4  If Steps 1 to 3 do not work, replace the voice interface card (VIC).
If Steps 1 to 3 do not work, replace the voice interface card (VIC).


































































No comments:
Post a Comment